|
page 3
Demonstrations of resistance to fire
In 1854, George set up his first public demonstration of the
fire-resistance of his safes. Public demonstrations were supposed to
prove that manufacturers' claims and advertisements were true. George
gives an account in his Treatise of this first demonstration, which he
asked a Milner's foreman to assist him in setting up.
"Soon after taking over the business of which I am now
proprietor, relying on the statements of other makers as well as on the
assurances of a person in my employ, as to the fire-resisting
capabilities of safes made fire-proof by the use of a simple
non-conductor (which activated the production of steam to preserve the
contents) I had a public test of two safes made on this principle and
invited my friends and fellow townsmen to be present a the trial.
One safe was in an intense fire for three hours, and the other for
five hours - Mr. Milner's foreman and his agent and lock manufacturer in
Wolverhampton were present and assisting me. The contents comprised
books, bound in leather, loose papers and a parchment deed. After the
safes were cooled and opened, the books were found to be burnt black at
the edge for some distance towards the centre of the paper; the loose
papers were more or less burned, the leather destroyed, and not a
vestige of parchment could be found. The disappointment, vexation and
chagrin I experienced at the result of this my first test, caused me to
study the manufacture, not only as a mechanical art, but as a science
requiring some research. From that day, it has had my undivided study
and attention."

| An old woodcut showing a public demonstration of
the security of a safe. In this case a group of German operatives
were failing to effect an entry despite all their equipment |
It was public humiliation which motivated him to write his huge book.
Milners had always claimed in their advertisements that their own safes
would protect "deeds" from fire. But they must have excluded
parchment deeds from their public tests. "It would invariably be
assumed (by the public) that 'deeds' meant parchment deeds, even though
the word parchment was excluded." George should have remembered
that Bilston's bonnet makers used to buy offcuts of parchment from his
father's print shop. Parchment is made from animal skin and the bonnet
makers used to boil it for size to stiffen bonnet brims. Steam could
never be used to protect parchment from heat. It was melted, cooked,
frazzled by steam. Paper, made from cotton waste and wood pulp,
survived, as did money and precious metals. What incensed George was
that Milner's foreman had allowed - perhaps encouraged - the novice safe
maker, himself, to include parchment in his first challenge, knowing it
would frazzle. (In writing about this, George says nothing about the
fact that Noakes' advertisements had also claimed to protect deeds.)
From there on George was on his high horse, the bit between his
teeth, hell bent on outdoing all competitors, and above all, William
Milner, son of Thomas, the founder of the company.
But George was not above sharp practice himself. Far from it! The
locks on Price's safes in the early days were made by Charles Aubin,
whose lock trophy had been purchased by Mr. Hobbs. Aubin had also worked
for Samuel Chatwood, another powerful competitor in the safe industry.
Later George patented Aubin's design as his own. Then there was the bad
feeling caused by recruiting William Dawes, again from Samuel Chatwood.
It was dog eat dog.
Developments at George Price's works

|
The 1903 Ordnance Survey Map
shows the Cleveland Works (here outlined in red) on the north side of
Cleveland Street and the east of Bell Street. This area was still
predominantly industrial at the time. |
All this time, George Price was working on converting Noakes' old
workshop to a steam-powered manufactory. The following item appeared in
the Wolverhampton Chronicle for June 20th 1855:
We have inspected the new works of Mr. Price and were as much
surprised as pleased with out visit .… The manufacture of wrought iron
safes we have always considered one of the legitimate trades of
Wolverhampton as it is well known that both the iron plates of which
they are made and the locks which secure them, are made in the
neighbourhood of the town. And yet, their manufacture has been almost
entirely confined to London and Liverpool .… We were very much pleased
with the machinery and fittings and also with the steam engine made by
Thompson and Co. of Bilston. The buildings are substantial, the rooms
wide, lofty and well ventilated. Crowding of workmen is completely
avoided. The iron of which the safes are constructed goes in at one end
of the building in sheets and comes out at the other end a finished and
painted safe, ready to be lowered into the carrier's wagon.
 |
By this time George felt he had overcome the problem with frazzled
parchment by patenting an iron box to hold parchment documents to be
placed inside his safes as protection against steam in case of fire.
He
had sixty men "at full work with the aid of steam machinery and
every contrivance which ingenuity could suggest". With governments,
bankers, insurance companies, railway companies desperate for security,
there was a lot of money to be made.
In 1855 he began to travel to give lectures on fire-resistant safe
manufacture in Edinburgh, Glasgow, Dublin and Belfast. "But for ill
health", he wrote, "I would have visited other towns and
cities in England." Instead of that, he sat down and wrote his
book. |
George Price's great treatise
George Price's 1,000 page book, Treatise On Fire And Thief-Proof
Depositories And Locks And Keys was published in 1856 by E. and F.N.
Spon. Charles Chubb had already written a Treatise on Locks, but
George's was much more detailed.
| It was highly praised, although some
bankers called it "The Burglars' Bible" because of the scores
of detailed diagrams of locks. George Price argued in the book that
progress would be speeded up if expertise were freely shared amongst
competitors.
But the locksmiths and safe manufacturers - including
himself - were just as ruthless as any burglar, forever stealing,
sometimes patenting, each others' ideas.
George also used the Treatise to advertise his own wares, even
though he had only been in the trade a very short time. He setup his own
"Which Safe?" survey, sending the specification for his own
"first class safes" - single and double door models - to his
competitors, asking them to quote their prices for similar safes. In a
table of prices given on pages 126 and 127, the George Price safes were
shown to be twenty five per cent cheaper than those manufactured by
Enemy No. 1 - Milner. Did he set his own prices before or after
receiving the other manufacturers' prices? Who's to say? Perhaps he set
his prices unsustainably low, in order to undercut his competitors. |

The title page to the
Treatise. The drawing on it is full of Masonic symbolism.
|
|

An illustration from the
Treatise, showing a device for picking Bramah locks |
The Cleveland Works went from strength to strength, specialising in
building strong rooms in the basements of the great banks being built up
and down the country, as well as manufacturing a great variety of
specialist safes with very fancy names:
the Super XB Commercial Safe,
the Merchant's Hold Fast Bent Steel
Commercial Coffer Safe,
the Everybody's Bent Steel Safe,
the Al Quality
for slight risks only Bent Steel Safe.
|
The war against Milner
After the publication of his Treatise, George Price set up fire
resistance demonstrations again and went on to be involved in more
spectacular challenges between safemakers to demonstrate that gunpowder
could or could not be inserted into the keyholes of their safes. This
son of a pious churchwarden had become quite a showman.
|
But tragedy struck in 1860, in Burnley. After one of
these gunpowder challenges, one of Milner's foremen packed the lock of
an old out-of-date Price safe with gunpowder and trundled it back into
the yard while the crowds was dispersing. He then lit the fuse, the safe
shattered and a little boy was killed by one of the shards piercing his
head.
At the inquest the Coroner expressed his view that
things had got out of hand and the challenges were a public danger. Both
George and Milner were full of remorse.
However, George soon invented another way of getting at Milner. He
set up his agents all over the country to inform him every time a Milner
safe was successfully burgled by one of the gangs of increasingly
violent and skilful robbers who were roaming the country. On hearing of
"successful" robberies, he planned to rush to the scene of the
crime, if he could, to denigrate Milner's name and to advertise his own
products as superior.
|

In his second treatise Price is careful to describe this as "Milner's
Phoenix Escutcheon, engraved from the one on the safe blown up in Burnley".
|
 |
In 1860 George published his second treaties "A
Treatise on Gunpowder-Proof Locks, Gunpowder-Proof Lock-Chambers,
Drill Proof Safes, &c, &c, &c.."
The Masonic symbolism from the first treatise is missing but there
is a quotation from Robert Blair: "Although there may be some few
exceptions, yet in general it holds that when the bent of the mind is
wholly directed to some one object, exclusive, in a manner, of others,
there is the fairest prospect of eminence in that, whatever it may
be. The rays must converge to a point in order to glow
intensely".
This claim to superiority of knowledge may be a suggestion that he
knew more about this matter than anyone else - including Milner. |
| In January 1863 a gang using skeleton keys entered the warehouse of a
woollen mill in Batley, Yorkshire. They tried breaking into the mill
safe, which contained a large amount of gold. They partially succeeded
but then lost patience with their implement, described as "the
largest burglar machine ever constructed", and began bashing the
safe with a crowbar.
They left their machine behind when the millowner
disturbed them. It was so massive that seven men had been needed to
carry it in pieces, to be attached to the safe at the scene of the
burglary.
Delighted with this find, the Dewsbury Constabulary put the
machine together and displayed it in the police station. As soon as his
agent told him of this, George Price contacted a Dewsbury company, who
had one of his safes, and arranged for it to be tested in public with
this great implement.
It survived the test without even a dent and
George's order book swelled again.
|

A drawing, from the second treatise,
showing "The burglars' drilling, boring and cutting
machine".
|
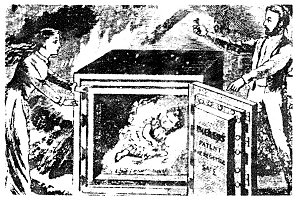
A baby, safe and sound, after a
fire. Presumably a fanciful notion - the baby would have
suffocated and been steamed. |
He eventually published in 1866 a short, vindictive book entitled
"Forty Burglaries of the years 1863-45", recording the regular
cracking of Milner safes. But, he boasted, when burglars drilled a hole
in the roof of a provision dealer in Kirkgate, Leeds, and saw a George
Price safe, they left without bothering to touch it. He recorded with glee a spectacular jewellery robbery from a shop in
Cornhill, London - from a Milner safe, of course. The safe was
advertised as "Holdfast" and "Thiefproof" and the
shop owner, Mr. Walker, sued Milners, his case being that it was
neither. |
A well-known cracksman, who George refers to as "Convict
Caseley", gave evidence that he could open a similar safe in half
an hour. "He is a man of keen wit, coarse in quality and
inexhaustible in quantity, that bubbled up like bad petroleum". He
showed "the instinct of an actor for effect; the craving of an
orator for applause; the delight of an artist in flattery." Caseley
described himself as "one of the dangerous classes who society had
found out and locked up". The cleverest men at the bar, says
George, were those most struck with the cleverness of the uneducated
Caseley. Indeed, it was a pity he could not be employed in Scotland Yard
- a thief set to catch thieves. But Mr. Walker lost his case, with the
judge ruling that he should have employed a watchman to watch his shop.
Presumably Convict Caseley's claim was not accepted, and the judge
commented that it took twenty four hours for the thieves to break into
the safe, proving it was "strong enough". The
press took up the judge's comments to condemn companies who did not employ watchmen to watch the safes
and called for an increase in the pay of policemen.
 |
 |
 |
| Return to the
last page |
Return to the
gazetteer |
Proceed to the
next page |
|

